The fields of health informatics and bioinformatics play key roles in shaping the future of healthcare and overcoming common challenges healthcare organizations face. While these disciplines may sound familiar, they serve a distinct purpose in their respective domains. Each area offers a diverse range of potential research and career opportunities.
What is Health Informatics?
Health informatics prioritizes improving patient care through the efficient management of patient data. Health informatics, considered the “backbone” of modern healthcare systems and processes, leverages various applications to collect, store, retrieve and use patient health information to facilitate efficient decision-making.
Health informatics encompasses a wide range of applications, some of which include:
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs) – Health informatics is crucial to the development and implementation of EHRs. The integration of EHRs helps healthcare providers with instant access to accurate patient information to promote better real-time decisions.
- Telemedicine – Health informatics helps develop secure and user-friendly telemedicine platforms to enhance accessibility and protect the integrity of patient data for virtual healthcare services.
- Health Information Exchange (HIE) – Patient information being shared between healthcare providers must be secure and efficient. Health informatics helps maintain the infrastructure for HIE for seamless and compliant exchange of patient information.
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) – These tools use analytics to provide healthcare providers with recommendations and alerts to potential threats in a patient’s treatment plan. Health informatics supports these systems to improve their accuracy and lead to better patient care.
What is Bioinformatics?
Bioinformatics is a field that integrates biology, computer science and information technology to analyze and interpret biological data. It involves the development and application of computational tools and methods for the storage, analysis and visualization of biological information, such as genomic data, protein structures and molecular pathways.
Bioinformatic tools are widely used to foster innovations in different areas such as drug discovery, personalized medicine and agricultural biotechnology. Bioinformatics is applied in a variety of fields of study, including:
- Genomic Sequencing – Bioinformatics helps with the analysis of entire genomes to help boost our understanding of genetics, evolution and genetic diseases.
- Proteomics – The field of proteomics focuses on the analysis of protein structures and functions. Bioinformatics helps support the facilitation of this research and leverages it towards the development of innovations and discoveries in cellular processes and drug discovery.
- Systems Biology – Bioinformatics is key in systems biology, which is an approach to understanding how biological systems work overall.
Differences Between Health Informatics and Bioinformatics
Health informatics and bioinformatics differ in many ways, namely their focus areas, data types and end goals.
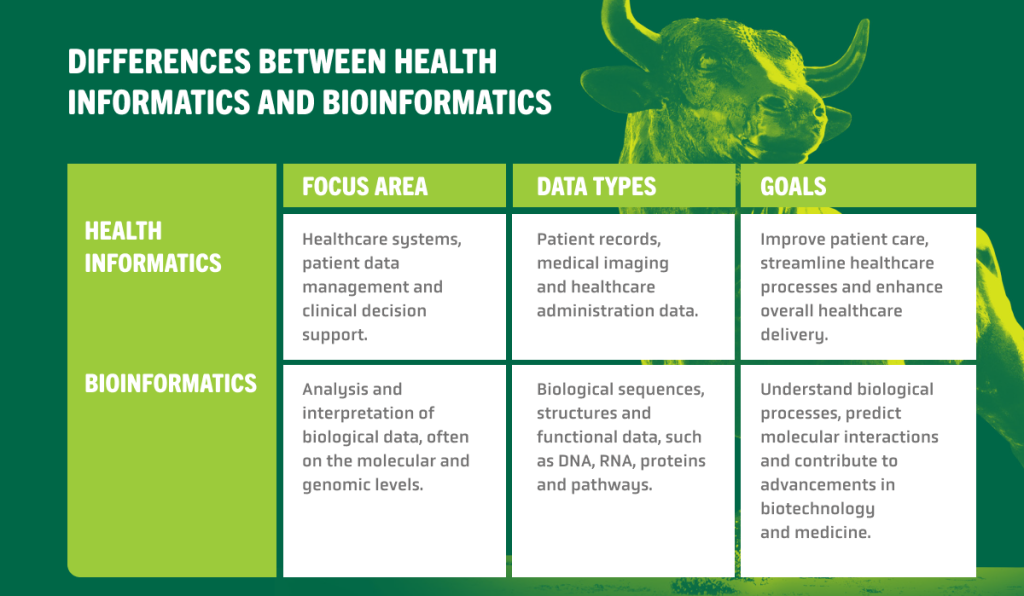
These two disciplines have distinctions in their purposes and applications, though they also share an important similarity. Both disciplines aim to leverage digital information technology to help enhance our understanding of health data so organizations and professionals can strive towards improving patient care and advancing medical research. Ensuring these disciplines are more closely integrated together while understanding their standalone purposes and uses can lead to potential innovations in healthcare services and empower organizations to optimize their approaches.
Research Opportunities in Health Informatics and Bioinformatics
Research in health informatics often involves improving healthcare systems, developing new technologies for patient care and evaluating the impact of information technology on healthcare outcomes. Health informatics professionals may also explore ways to integrate emerging technologies such as AI and machine learning into healthcare organizations and processes. Health informatics research would align well with those who are more interested in improving patient care and finding new ways to leverage emerging technologies for more optimized patient outcomes.
Research in bioinformatics focuses on understanding biological systems, analyzing large-scale genomic and proteomic data and contributing to fields like personalized medicine and synthetic biology. This means research opportunities fall in the more technical realm of healthcare, like developing new algorithms for analyses or exploring the relationships between a variety of biological components working together. Bioinformatics research can typically appeal more to those interested in working with the complexities of biological data and its applications towards driving innovations and discovery.
Career Outlook for Health Informatics and Bioinformatics
Career opportunities in the field of health informatics are expected to grow over the next decade as healthcare organizations continue to prioritize data security and leverage insights towards enhancing patient care. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment of health information technologists and medical registrars is projected to increase 16% from 2022 to 2032, much faster than the national average for all occupations. Other career paths include roles such as:
- Health Information Manager
- Clinical Informatician
- Healthcare IT Consultant
- Systems Analyst
Bioinformatics career paths can vary for individuals with backgrounds in biology and computer science. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment of computer and information research scientists is projected to grow 23% from 2022 to 2032, much faster than the average for all other occupations. Potential career paths include roles such as:
- Bioinformatics Analyst
- Computational Biologist
- Research Scientist
- Bioinformatics Software Developer
Specialize Your Future in Healthcare with USF Health
Understanding the distinctions between health informatics and bioinformatics is crucial when considering a career in health or biological sciences. Both informatics fields offer exciting research and career opportunities, catering to those invested in improving patient care or contributing to cutting-edge biological research.
Our graduate programs in health informatics, designed by leading healthcare professionals and delivered by distinguished faculty, offers a comprehensive pathway for professional growth and expertise. These programs equip aspiring and current healthcare professionals with critical skills and knowledge, essential for navigating and contributing effectively to the dynamic health sector.




